Mastering Diabetes: Unraveling the Secrets of Self-Management
Diabetes is not just a medical issue; it’s a way of life that demands constant attention and care. Mastering diabetes management can help individuals lead happy, healthy lives without diabetes taking the front seat.
Understanding Diabetes Self-Management
Diabetes self-management entails the methods and habits perons with diabetes adopt to take control of their condition effectively. This includes monitoring blood sugar levels, administering medications, and making important lifestyle changes. Grasping how these elements work together is vital for ensuring long-term health.
Education is the starting point for effective self-management. Understanding the differences between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is essential. For example, individuals with Type 1 diabetes must closely monitor their insulin intake, while those with Type 2 often focus on adjusting their diet. Studies show that patients who are educated about their condition tend to have better control over their blood sugar levels, leading to fewer complications.
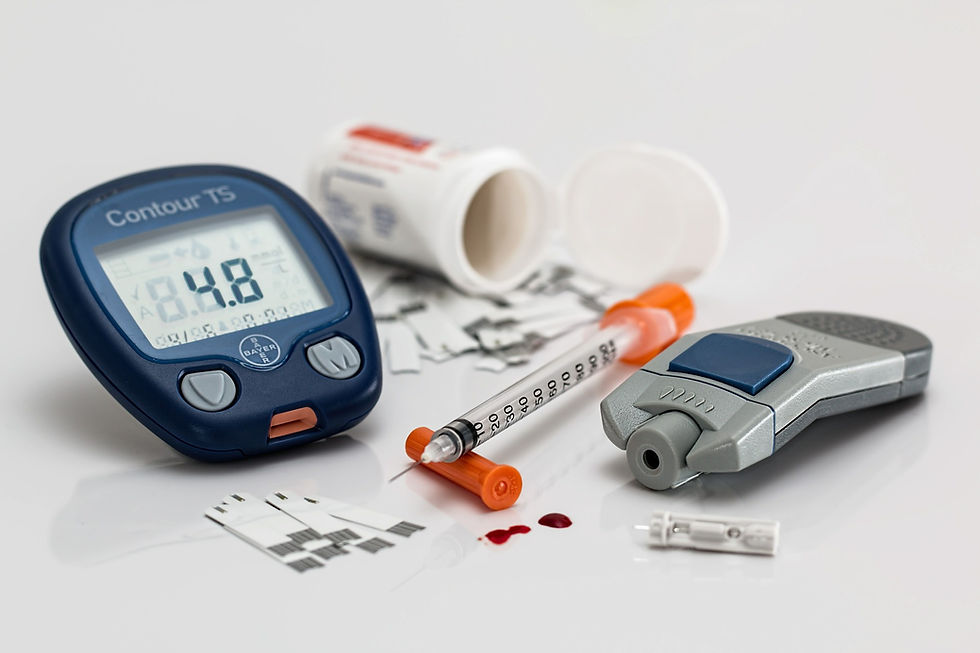
The Importance of Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels is fundamental to successful diabetes self-management. Using a glucose meter is one of the simplest ways to keep track of your levels throughout the day, providing insights into how various factors like food, exercise, and stress impact your blood sugar. Keeping a log of these readings enhances communication with your healthcare team, allowing them to tailor your treatment plan more effectively.
Nutrition: Fueling Your Journey
Nutrition is crucial in diabetes management. A diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Carbohydrate counting enables you to understand how different foods affect your glucose levels. For example, pairing 30 grams of carbohydrates with a source of protein like grilled chicken or salmon slows sugar absorption, leading to steadier blood sugar levels. This method can help individuals manage their diabetes more effectively.
Physical Activity: Movement Matters
Regular physical activity is a key component of diabetes self-management. Engaging in aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling helps improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, combined with strength training exercises at least twice a week. These activities can significantly lower blood sugar levels and overall health risks.Before beginning any new physical activity, it’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider. They can give you tailored advice based on your current health status and fitness level.
Stress Management and Support
Managing stress is often an overlooked yet critical element of diabetes self-management. Stress can lead to higher blood sugar levels, making it essential to incorporate stress-reduction activities into your routine. Practices like mindfulness, yoga, and even engaging in hobbies can be beneficial.
Building a support network can also play a significant role in managing diabetes. Family, friends, or diabetes support groups can offer emotional support and shared experiences, providing comfort and fostering resilience. Studies show that individuals with a support network are more likely to maintain healthier lifestyles and better manage their diabetes.
Taking Charge of Your Health
Mastering diabetes self-management can feel overwhelming, but with the right knowledge, discipline, and support, you can achieve it. By prioritizing education, monitoring, nutrition, physical activity, and stress management, you can gain control over your health and lead a fulfilling life. Remember, even small steps towards effective self-management can make a dramatic difference in your diabetes journey.
With the right ongoing education and support, managing diabetes can shift from a daunting task to a manageable part of your life. Embrace the strategies of self-management and take control of your health today!

























Comments